Photo by Carlos Muza on Unsplash
A Beginner’s Guide to Data Engineering: Understanding the Core Components
Introduction
With the rise of the internet and modern technologies, a huge amount of data is being generated every second. As this data brings great value to business organizations, an ability to understand and work with such a vast amount of data is much needed for organizations in the present world. Data engineering is a field that grants us this much-needed ability. Simply saying, data engineering is a field that deals with the use of specialized tools and techniques to transform raw data from various sources into meaningful and valuable information. It involves designing, building and managing the infrastructures that support the collection, storage, processing and analysis of large volumes of data. The information generated from data engineering helps in making business decisions. Data engineering is a crucial aspect of data science and analytics and is important for every data-driven organization in the modern world. In this blog post, I will provide a simple and concise overview of data engineering concepts, including its main components with some examples.
Components of Data Engineering
Data engineering is the process of designing, building, testing, and maintaining the architecture and infrastructure necessary for processing and storing large volumes of data. It involves a variety of components, including data ingestion, data transformation, data storage, data retrieval and data visualization. These components work together to create data infrastructures like ETL pipelines that transform raw data into valuable information. The following figure illustrates the core components of data engineering.
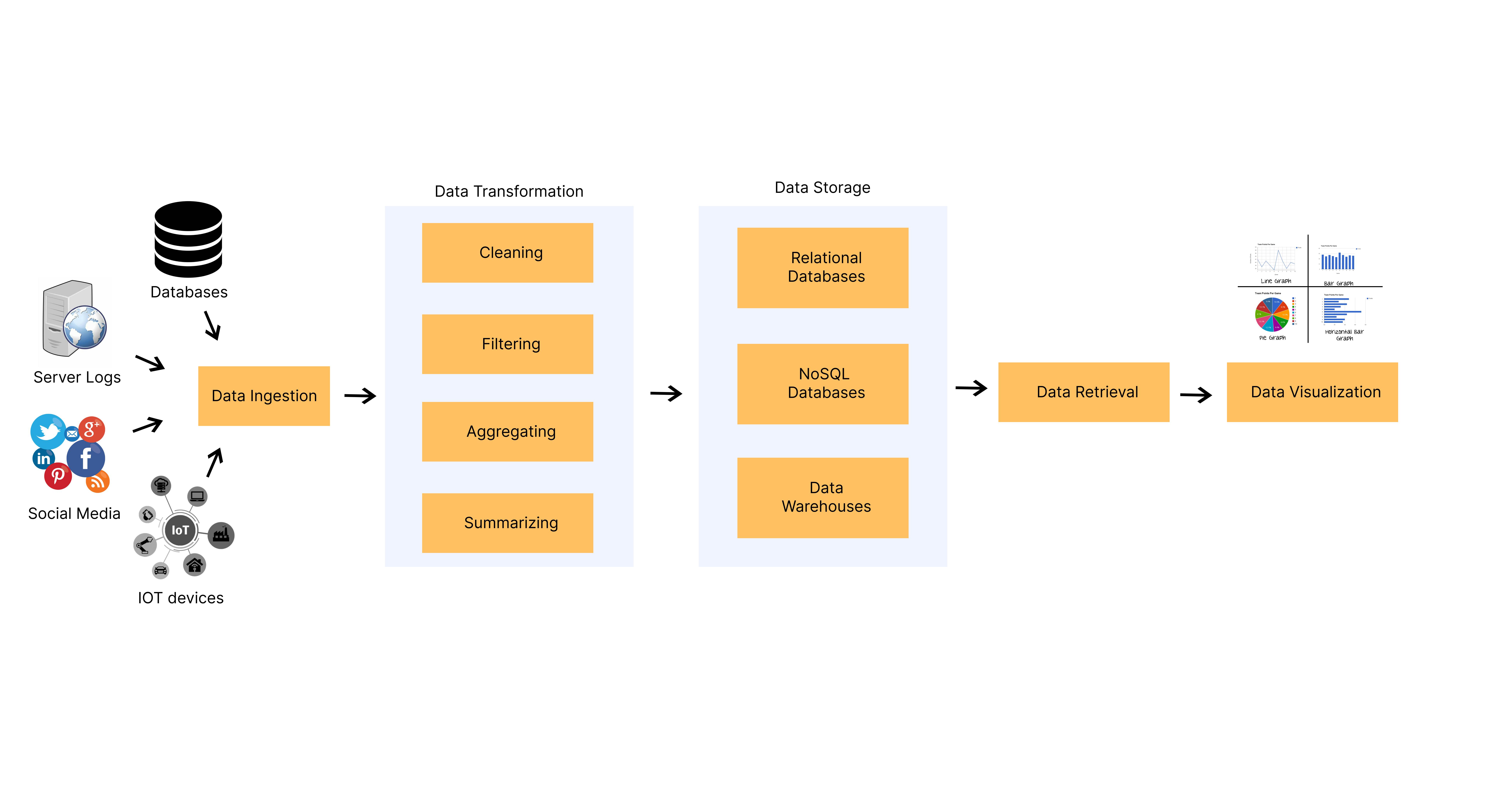
Figure: Core Components of Data Engineering
1. Data Ingestion
Data ingestion simply means data collection. It is the process of collecting and capturing data from various sources and then converting the data to a format that can be easily processed and stored. Data ingestion is the first step in data engineering. The various data sources for data ingestion can include the organization’s operational database, APIs, internet, IOT systems, server logs, social media platforms etc.
For example, a company may collect server logs, transform them to a suitable format and then store it in a data warehouse which can be later used for analysis and anomaly detection.
2. Data Transformation
Data transformation is the process of converting raw data into a format that is suitable for analysis. This involves cleaning, filtering, aggregating, and joining data from various sources. Normally, Python libraries like pandas can be used for data manipulation and transformation, but in the context of big data, tools like Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and Apache Flink are used for data processing and transformation.
For example, the raw data may consist of the price of products in euros and various duplicate and unwanted columns. Data transformation can include converting price to dollars, and selecting only the necessary columns by removing duplicate and unwanted columns to convert data to a suitable format for analysis.
3. Data Storage
Data storage is the process of storing data in a way that is optimized for querying and analysis. It involves selecting an appropriate database or data warehouse based on the type of data, designing schema to reflect the organization of data and organization and management of data within the storage system. Traditionally, relational databases have been used for storing structured data but due to the increase in unstructured and semi-structured data on the internet, NoSQL databases are widely used at present. Also, data warehouses are used for storing historical data for analysis. The choice of storage system depends on the volume, velocity, and variety of data being processed.
For example, A company can store historical data related to customers’ purchases and their interests in a data warehouse and later use this data for analysis and creating personalized recommendation systems for customers.
4. Data Retrieval
Data retrieval is the process of accessing and retrieving data from storage for analysis. This step involves querying the data stored in databases and data warehouses using SQL queries or using specialized tools.
For example, the data stored in a relational database can be retrieved using SQL queries and then analyzed using a business intelligence tool
5. Data Visualization
Data visualization involves the representation of data in a visual format, such as charts, graphs, and dashboards. This allows data analysts and business users to gain insights into data quickly and make informed decisions based on the data. Popular data visualization tools include Tableau, Power BI, etc.
For example, Customer data may be visualized in the form of a scatter plot, which can help analysts group customers with similar interests. This can help generate various insights and also help in building recommendation systems for customers.
Conclusion
Data engineering is a complex and rapidly growing field, but understanding its main components is essential for any organization that wants to use data for business insights and decision-making. It involves a range of tasks, including data ingestion, data transformation, data storage, data retrieval and data visualization. By designing and maintaining a robust data engineering infrastructure, organizations can ensure that their data is accurate, reliable, and easily accessible for analysis which drives innovation and growth.
Epilogue
I am a recent computer engineering undergraduate and am highly interested in the data and AI field. I recently started learning data engineering, and I am writing blogs to share my learning. This is my first blog in the data engineering series, and I hope you enjoyed reading this. I will be writing more blogs related to data engineering soon, so stay tuned. This is the way ☄️.